Constant, high-pitched ringing may reflect nerve irritation or prolonged stress.
Low, pulsating hums can indicate vascular turbulence — sometimes associated with high blood pressure or anemia.
Sudden-onset tinnitus can occur after exposure to loud sounds or due to medication side effects (especially certain antibiotics or anti-inflammatories).
In holistic medicine, tinnitus is sometimes described as the body’s “alarm bell,” warning that internal harmony has been disrupted — whether by emotional stress, toxicity, or circulatory imbalance.
If your tinnitus fluctuates with stress, diet, or caffeine, it’s a strong sign that your nervous system and vascular function are at play.
Balance and Dizziness: The Ear’s Role in Whole-Body Coordination
The inner ear does more than interpret sound — it governs your sense of balance. Inside the labyrinth of the inner ear are fluid-filled canals lined with hair-like sensors that detect movement and orientation.
When this system malfunctions, it can lead to dizziness, vertigo, or disorientation. These symptoms often point to deeper health issues such as:
Low blood pressure or dehydration
Iron deficiency
Viral infections or inflammation (labyrinthitis)
Autoimmune disorders affecting the inner ear (Ménière’s disease)
Nerve dysfunction due to diabetes or B12 deficiency
Because balance depends on coordination between the ears, eyes, and brain, persistent dizziness or unsteadiness should always be viewed as a full-body signal, not just a local ear problem.
Emotional Health Reflected in the Ears
Our ears don’t just mirror physical health — they respond to emotional and psychological states as well.
During moments of embarrassment, anxiety, or anger, the ears can flush red due to the release of adrenaline and increased blood flow. Chronic stress can trigger ear tension, itching, or sensitivity as the body remains in a heightened state of alert.
In many traditional healing philosophies, the ears are seen as symbolic of listening — both to the world and to oneself. Ear-related issues may metaphorically indicate inner conflict, resistance, or emotional overwhelm.
While science focuses on physical mechanisms, the overlap between emotion and biology here is undeniable. Stress hormones, after all, directly affect blood vessels, nerves, and immune responses — all of which influence ear health.
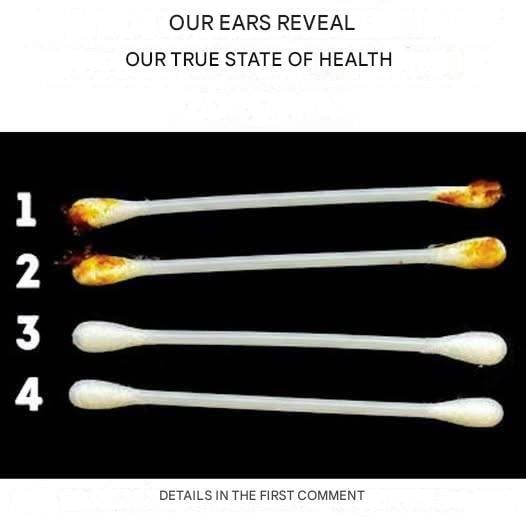
Ear Wax: A Natural Health Indicator
Earwax (cerumen) is often viewed as a nuisance, but it’s actually one of the most telling — and protective — substances your body produces. Its texture, color, and amount can say a lot about your overall well-being.
Dry, flaky wax may be linked to dehydration or low-fat diets.
Sticky, dark wax often appears in people with higher perspiration levels or those under stress.
Excessive buildup can indicate poor detoxification, allergies, or overactive oil glands.
A sudden change in wax consistency may be a reaction to diet, medication, or hormonal fluctuation.
Healthy earwax is slightly sticky and golden — a sign that your ears are effectively trapping dust, microbes, and toxins. The key is moderation: too little wax leaves your ear vulnerable to infection, while too much can block sound and create discomfort.
see continuation on next page